NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Questions and Answers, We have compiled the NCERT Class 7 Science Book Solutions for all topics in a comprehensive way to support students who are preparing effectively for the exam. You will discover both numerical and descriptive answers for all Chapter concepts in this NCERT Science Solutions pdf. Make use of this perfect guide and score good marks in the exam along with strong subject knowledge.
You can get answers of Nutrition in Plants class 7 solution, Nutrition in Plants class 7 pdf, Nutrition in Plants questions and answers, So explore this page.
Queries – ncert class 7 science chapter 1 nutrition in plants pdf, Ncert class 7 science chapter 1 nutrition in plants solutions, Ncert class 7 science chapter 1 nutrition in plants notes, science class 7 chapter 1 question answer science class 7 chapter 1 pdf, Ncert class 7 science chapter 1 nutrition in plants questions, nutrition in plants for class 7 pdf, Ncert class 7 science chapter 1 nutrition in plants answer
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Solution
Textual Exercise
Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Solution (Page 9)
Think and Do
Q. 1. Why do organisms need to take food?
Answer : Food is needed by all organisms for many purposes:
(a) The main function of food is to help in growth.
(b) Food provides energy for movements such as running, walking or raising our arm.
(c) Food is also needed for replacement and repairing damaged parts of body.
(d) Food gives us resistance to fight against diseases and protects us from infections
Q. 2. Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph.
Answer : Parasite – Parasite feeds on a living organism. The parasite on its feeds is called host.
Saprotroph: They feed on dead and decaying organisms. They do not fee on living organisms.
Q. 3. How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Answer : The presence of starch in leaves can be tested by Iodine test. When we remove chlorophyll from leaf by boiling it in alcohol and then put 2 drops of iodine solution, its colour change to blue indicates the presence of starch.
Q. 4. Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
Answer : The green plants have chlorophyll in the leaves. The leaves use C02 and water to make food in presence of sunlight.

Q. 5. Show with the help of a sketch that the plants are the ultimate source of food.
Answer :
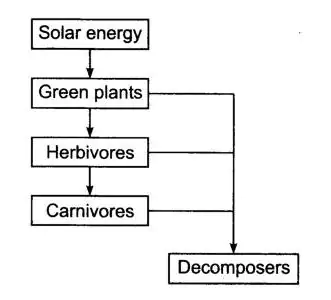
Q. 6. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Green plants are called ____ since they synthesise their own food.
(b) The food synthesised by the plants is stored as ____ .
(c) In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called ____
(d) During photosynthesis plants take in ____ and release ____ .
Answer : (a) autotrophs (b) starch (c) chlorophyll (d) carbon dioxide, oxygen
Q. 7. Name the following:
(i) A parasitic plant with yellow, slender and branched stem.
(ii) A plant that is partially autotrophic.
(iii) The pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Answer : (i) cuscuta (ii) Insectivorous plant (iii) Stomata
Q. 8. Tick the correct answer:
(a) Amarbel is an example of:
(i) Autotroph (ii) Parasite (iii) Saprotroph (iv) Host
(b) The plant which traps and feeds on insects is:
(i) Cuscuta (ii) China rose {iii) Pitcher plant (iv) Rose
Answer : (a) (ii) Parasite (b) (iii) Pitcher plant
Q. 9. Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II:
| A | B |
| (i) Chlorophyll (ii) Nitrogen (iii) Cuscuta iv) Animals (e) Insects | (a) Rhizobium (b) Heterotrophs (c) Pitcher plant iv) Leaf (e) Parasite |
Answer :
| A | B |
| (i) Chlorophyll (ii) Nitrogen (iii) Cuscuta (iv) Animals (v) Insects | (a) Leaf (b) Rhizobium (c) Parasite iv) Heterotrophs (e) Pitcher plant |
Q. 10. Mark T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(i) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (T/F)
(ii) Plants which synthesise their food themselves are called saprotrophs. (T/F)
(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein. (T/F)
(iv) Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T/F)
Answer : (a) F (ii) F (iii) T (iu) T
Q. 11. Choose the correct option from the following.
Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
(i) Root hair (ii) Stomata (iii) Leaf veins (iv) Sepals
Answer (ii) Stomata
Q.12. Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
(i) Roots (ii) Stem (iii) Flowers (iv) Leaves
Answer (iv) Leaves
Q.13. Why do farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large green houses? What are the advantages to the farmers?
Answer : Farmers grow fruits and vegetable crops inside large greenhouses for several reasons:
- Controlled Environment: Greenhouses allow farmers to control environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and light, optimizing conditions for plant growth.
- Protection: Greenhouses shield crops from adverse weather conditions, pests, and diseases, reducing crop loss and the need for chemical pesticides.
- Increased Yield: The controlled environment of greenhouses leads to higher crop yields compared to open-field cultivation.
- Water Efficiency: Greenhouse systems use water-efficient irrigation methods, minimizing water waste and maximizing water use efficiency.
- Improved Crop Quality: Greenhouse-grown crops often have better quality, appearance, and shelf life due to reduced exposure to environmental stresses.
- Season Extension: Greenhouses enable farmers to extend the growing season, producing crops year-round and increasing availability to consumers.
Overall, greenhouse cultivation offers farmers sustainable and efficient methods to produce high-quality fruits and vegetables while mitigating risks associated with weather and pests.
Hope you’ve got all the Solution in this page and find this NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Solution useful for exam preparation. Please share with others who need this.
Related Searches
- Chapter 1. Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 2. Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3. Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4. Heat
- Chapter 5. Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6. Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7. Weather; Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8. Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9. Soil
- Chapter 10. Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11. Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12. Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13. Motion and Time
- Chapter 14. Electric Current and its Effects
- Chapter 15. Light
- Chapter 16. Water; a Precious Resource
- Chapter 17. Forests; Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18. Wastewater Story
- NCERT Class 7 Science